In this article, I’ll show you how to apply Unity C# 7.0: ref locals & returns to simplify your game code and make your programming intentions clear when you deal with C# value types.

1. What a Bloody Mess!
Let’s say you’re developing a MMO (somehow a favorite for new game developers) and you’re currently programming a cheat to level up your character.
You know, faster development iterations.
So you have your PlayerStats structure, and also a Player class that contains its name and an instance of PlayerStats:
class Player
{
public string name;
public PlayerStats stats;
}
struct PlayerStats
{
public int level;
public int wrinkles;
}
Why a structure?
In my opinion, it generally makes sense to pack data into structures* because of the benefits of value types:
- Being value types, they are copied most of the time when passing it around. Your data remains more protected.
- Value types are often placed in the stack, meaning that you alleviate some of the pressure the garbage collection suffers from.
*Classes vs structures in game development is a tricky topic in itself. If you want to discuss that further, I’d be more than happy to: ruben@thegamedev.guru
In any case, this post not about this use case. It is about how this C# feature can benefit your use case.
Our cheat function will level up the character by increasing the player stats the following way:
- We add one to the current level.
- We add a few nasty wrinkles on the character’s face.
I know, very original gameplay mechanics that you can copy for your next MMO.
So your level up cheat function looks like this:
private void Cheat_LevelUpPlayer()
{
const string playerName = "Duncan";
var youngDuncan = GetPlayerStats(playerName);
Assert.IsTrue(youngDuncan.wrinkles == 0, "Young Duncan should have no wrinkles!");
// Level up
youngDuncan.level++;
youngDuncan.wrinkles += 5;
var oldDuncan = GetPlayerStats(playerName);
Assert.IsTrue(oldDuncan.wrinkles > 0, "Old Duncan should have at least a wrinkle!");
Debug.Log("Duncan aged successfully");
}
And this is the function that gives you the player stats:
private PlayerStats GetPlayerStats(string playerName)
{
var player = _players.Find(searchedPlayer => searchedPlayer.name.Equals(playerName));
return player.stats;
}
Now, if you know the difference between value types and reference types, you’d be right at saying “this won’t work as you expect, my friend“.
PlayerStats is a value type (it’s a structure). That means, C# will copy that instance for you when you return its value. Just to be safe.
So what happens is simple: no matter how you change the youngDuncan variable, it will never affect the original value stored in your list of players.
Traditionally, there are a few options to modify the values of PlayerStats:
- You can access the list directly by asking for an index instead of for a value.
- You can also declare a second parameter of type “ref PlayerStats“.
Those options will make your code dirtier.
And you don’t want dirt at home.
2. Solving the Mess With Ref Locals & Functions
Here’s an easier solution: just return a reference to the PlayerStats structure.
I know, PlayerStats is a value type (a structure) that is always copied when you pass it around.
But we can politely ask C# to return it as a reference.
Hey C#, would you mind giving me a reference instead of a value?
And it turns out it is very straight-forward thing to do: just use the ref keyword when returning it and when receiving it.
See for yourself:
private ref PlayerStats GetPlayerStatsRef(string playerName)
{
var player = _players.Find(searchedPlayer => searchedPlayer.name.Equals(playerName));
return ref player.stats;
}
private void Cheat_LevelUpPlayer()
{
const string playerName = "Duncan";
ref var youngDuncan = ref GetPlayerStatsRef(playerName);
Assert.IsTrue(youngDuncan.wrinkles == 0, "Young Duncan should have no wrinkles!");
// Level up
youngDuncan.level++;
youngDuncan.wrinkles += 5;
var oldDuncan = GetPlayerStats(playerName);
Assert.IsTrue(oldDuncan.wrinkles > 0, "Old Duncan should have at least a wrinkle!");
Debug.Log("Duncan aged successfully");
}
Here, we “just” added the ref keyword in four different places:
- Line 1: ref before the return type of the function
- Line 4: ref after the return keyword
- Line 11: ref before the variable type and before the function invocation.
Yes, it’s a bit over the top. I guess Microsoft really wanted us to be clear about our intentions.
If we now run the code, we will see that Mr. Duncan aged successfully.
Old Duncan has now a few wrinkles more… The price of experience.
3. Do C# Local References Make a Performance Difference?
Using references makes your code (slightly) cheaper, because we skip copying entire values.
Let’s do a small comparison:
private void Compare()
{
const string playerName = "Duncan";
var youngDuncanCopy = GetPlayerStats(playerName);
ref var youngDuncanRef = ref GetPlayerStatsRef(playerName);
youngDuncanCopy.level++;
youngDuncanRef.level++;
}
Let’s translate the C# code into beautiful IL code:
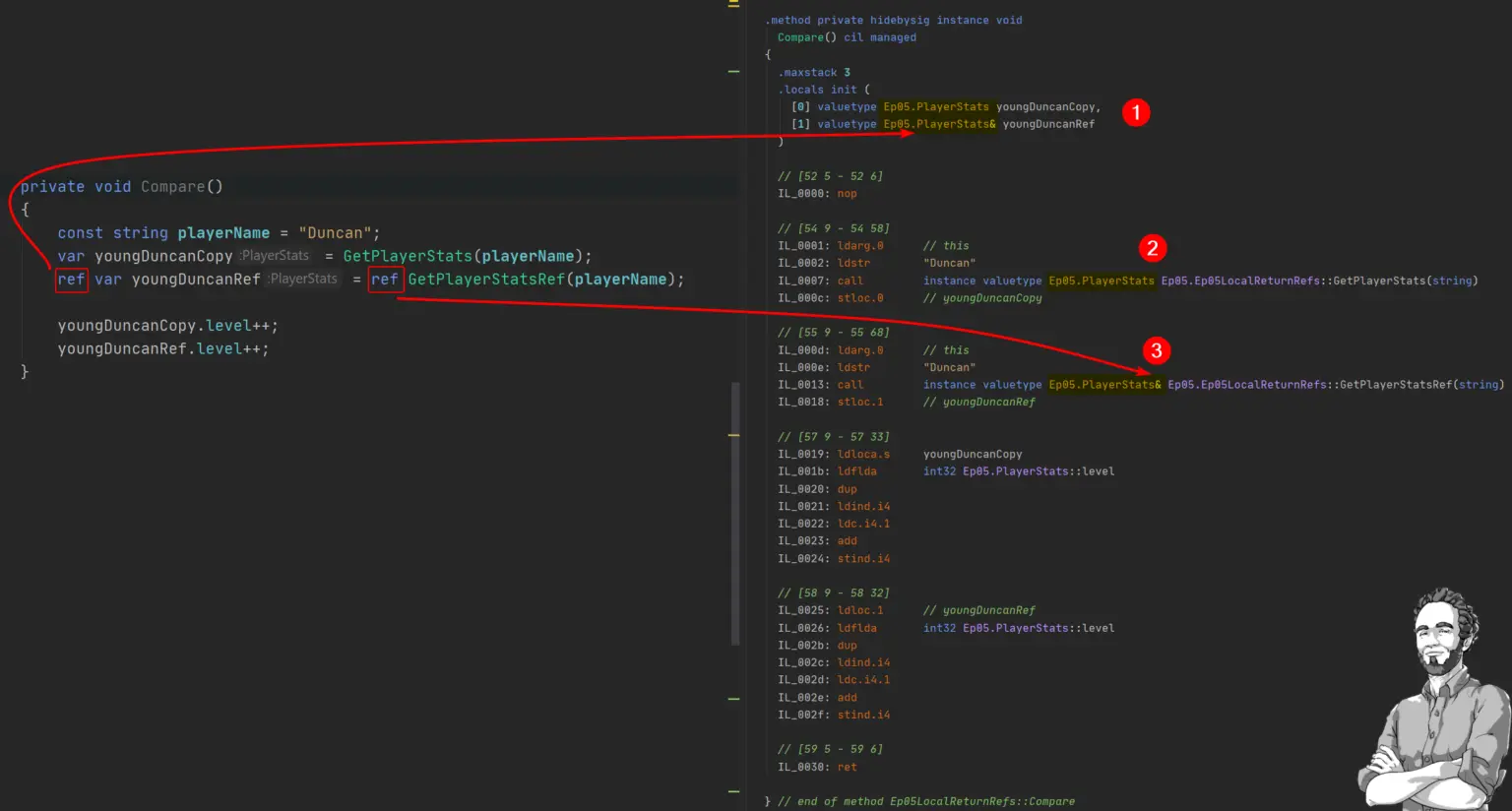
The IL codes are very similar but they have subtle changes that make all the difference:
- The youngDuncanCopy variable is just that, a whole new PlayerStats structure. However, youngDuncanRef is a reference to another PlayerStats variable (the & symbol denotes reference).
- When calling GetPlayerStats, we ask for a copy of the variable the function returns (no &).
- When you call GetPlayerStatsRef, we are actually getting a reference to that variable (see the & symbol).
You might wonder: how different are the functions themselves?
Here’s the answer:
- GetPlayerStats (copy) uses the IL instruction ldfld to load the value of the stats field.
- GetPlayerStats (ref) uses the IL instruction ldflda to load the address of the stats field.
So there you have it. A cheaper alternative at your disposal.
Lastly, be careful with this technique.
Using C# refs also makes your code unsafer, because now you have the power to modify the state of your game more easily.
Your choice.
Get the Unity Performance Checklist
Sign up to access the checklist and companion resources in your members area.
Already a member? Open this resource.
What’s Next?
If running your game at 60 FPS is something you would like, you’ll love my Unity Game Performance Checklist.
This list has over 100 action items that you can execute on to increase the performance of your game.
Low performance is painful for your players and your wallet. So don’t with anything below 60 FPS.
Grab my Unity Performance Checklist now.
…And start optimizing your game.
~Ruben

