In this blog post, I will show you why, when and how you should use LOD in Unity.
Remember: Level of Detail (LOD) is not only about the poly count!

Why Do You Need LODs in Your Unity Project?
Let's start with the obvious question: why might you need to use the Level of Detail technique in your Unity project?
Put simply, here are three reasons:
- Your project performance is bound by GPU - more specifically, by the vertex shading stage.
- You are suffering by too many draw calls, effectively having a big CPU cost in the rendering section.
- Geometric aliasing: Your high-poly meshes look jittery and aliased when seen from the distance.
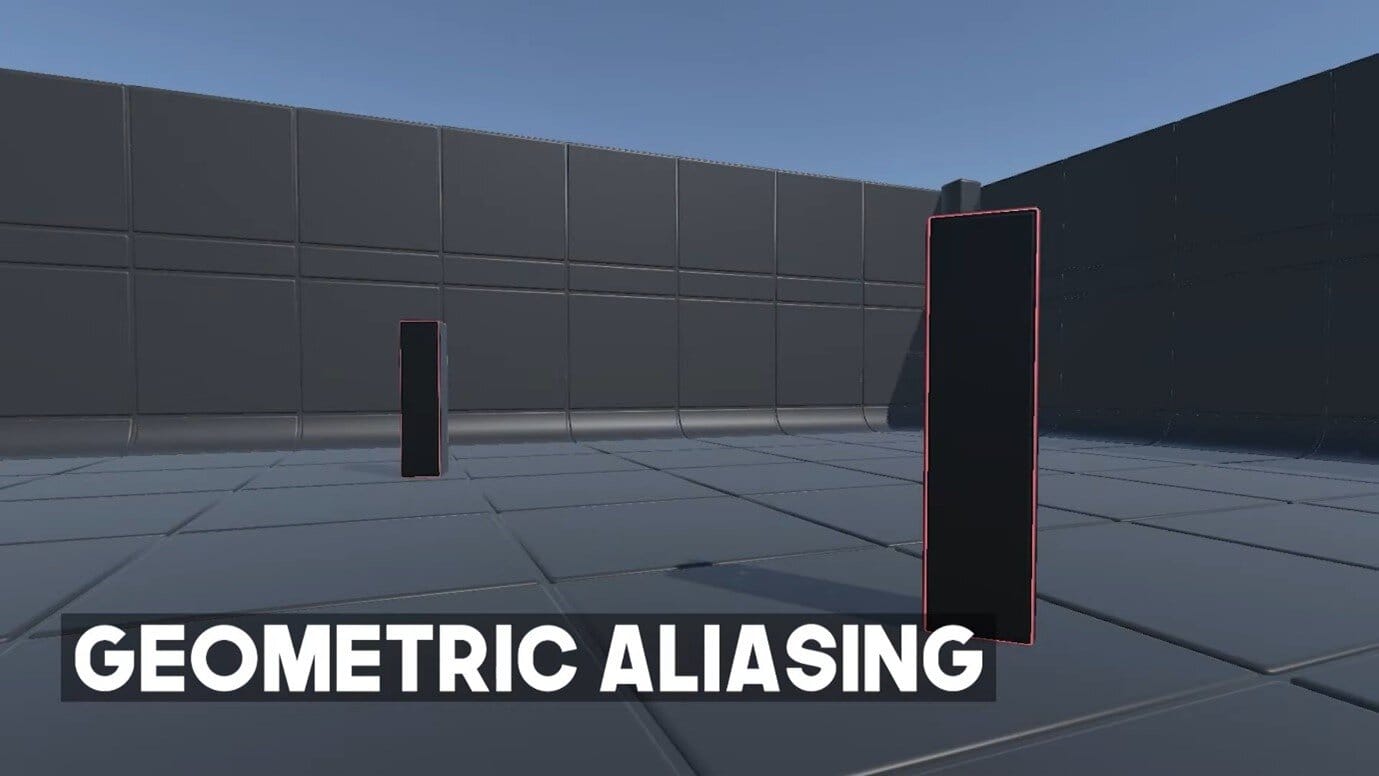
If you are in any of the three situations, then here's your green light to use the Unity LOD feature.
Let's see what exactly it is.
What is LOD or Level of Detail in Unity?
The Level of Detail you'd use in Unity is rather simple. It's just about changing the mesh you render at different distances from your camera.
This is the logic behind using juicy LODs in Unity:
- The closer you are to an object, the more detail you need to represent it faithfully, i.e. you can see more of it.
- The more far away you get from an object, the less detail you need to represent it faithfully.
In reality, it's not so much the distance from the camera to the object, but the size the object occupies in the screen in pixels.
But yes, that size is reduced when you move away from the object.
This is no different from real life. When you zoom in in a picture, you can see all the spots in someone's face. That's why it's a good idea to shrink a bad selfie so that no one can see the wrong details.
LOD Example by ev1lbl0w
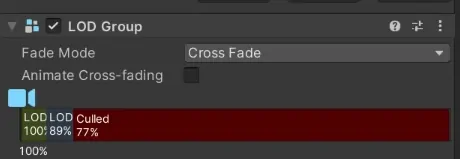
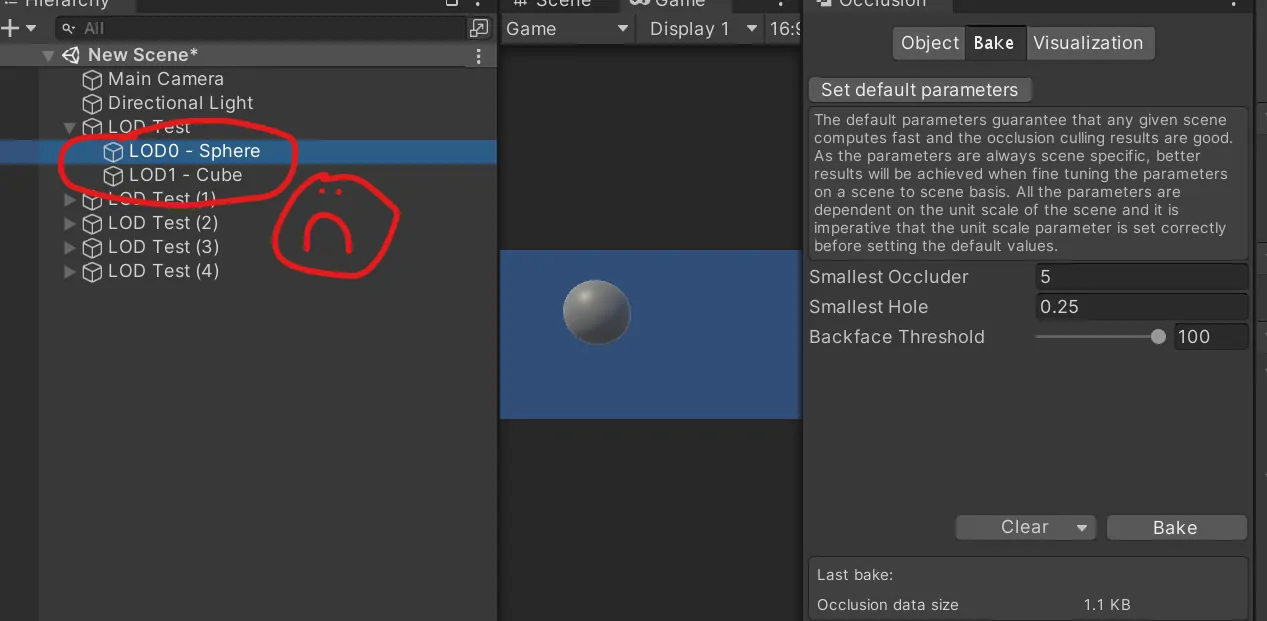
The Unity LOD system has a series of "levels":
- LOD0 is the most detailed version of your mesh. You want to use it when your player sits in front of it to appreciate all its features.
- LOD1 is a less detailed version that commonly has fewer vertices and polygons. You use it when your user gets more far away.
- LOD2 is a low-detail version of your mesh, used when the object is far away.
- Culled: once your object is too far away, you can decide to skip rendering it at all.
You can introduce more LOD levels, but having three levels or even two is often more than enough.
Now, how do you use LODs?

How to Use LOD in Unity: The Basics
The basics are straight forward:
- Create different resolutions of your meshes (lower/higher depending on your current mesh).
- Add LODGroup component to an empty parent object.
- Add mesh renderers + filters as child gameobjects.
- Assign them to different LOD levels in the LODGroup component.
- Tweak distance thresholds between LOD levels.
Unity will then automatically switch between your LOD levels depending on its distance to the camera for you.
Let's see those, step by step.
1. Generate LOD Variations: Your Options
To generate the different versions of your LODs, you have three options:
- A) Manual
- B) Automagically
- C) Quick & Dirty
The difference between them is the time you'll put into them, the resulting quality you get and the flexibility you have in the process.
A) Manual LOD Generation
Here, it is all about editing your meshes in your favorite 3d software (Blender you said?).
There are universal modifiers that help you here, such as decimate/subdivide, but most of the time you have to edit the result to make it sexy.
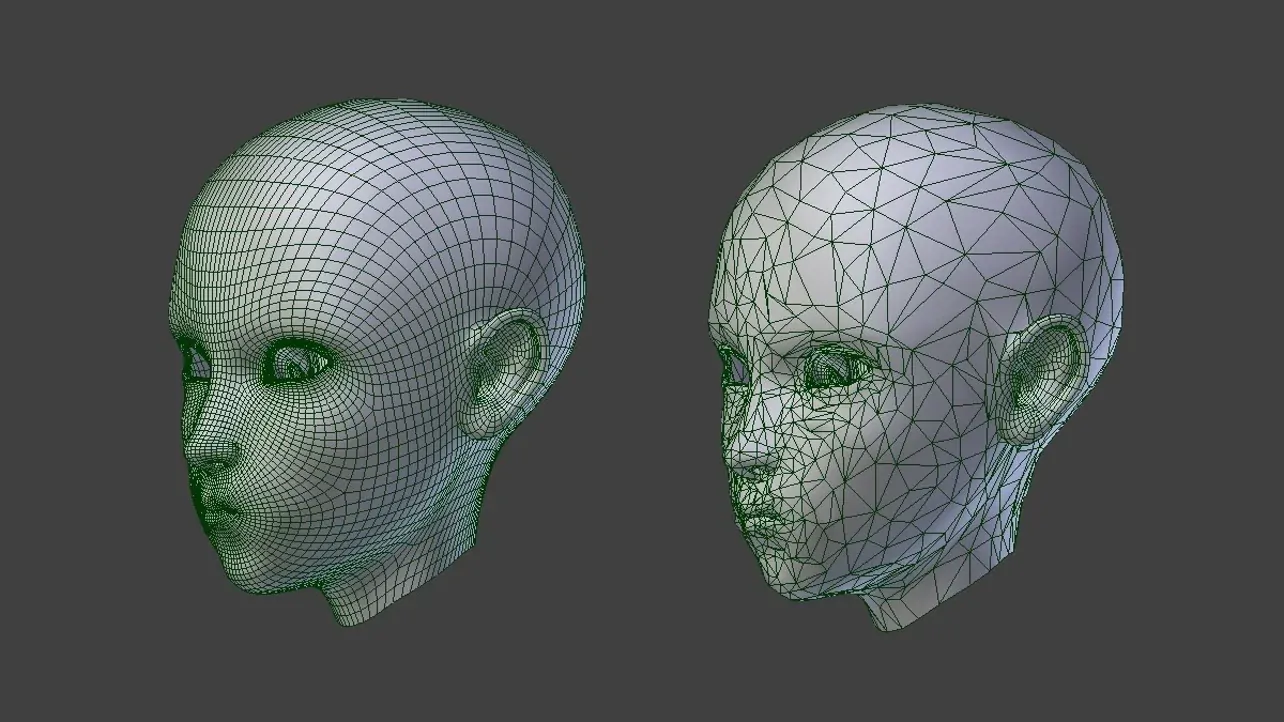
This is more of an art thing and I am no artist, so let's get into the programmer-friendlier way.

B) Automagically Generation of LODs
Here we enter in the realm of specialized LOD generation tools... often called "automatic LOD" (but that's almost never the case).
The idea is simple: let smart software generate the LOD levels for you.
Here are some of them:
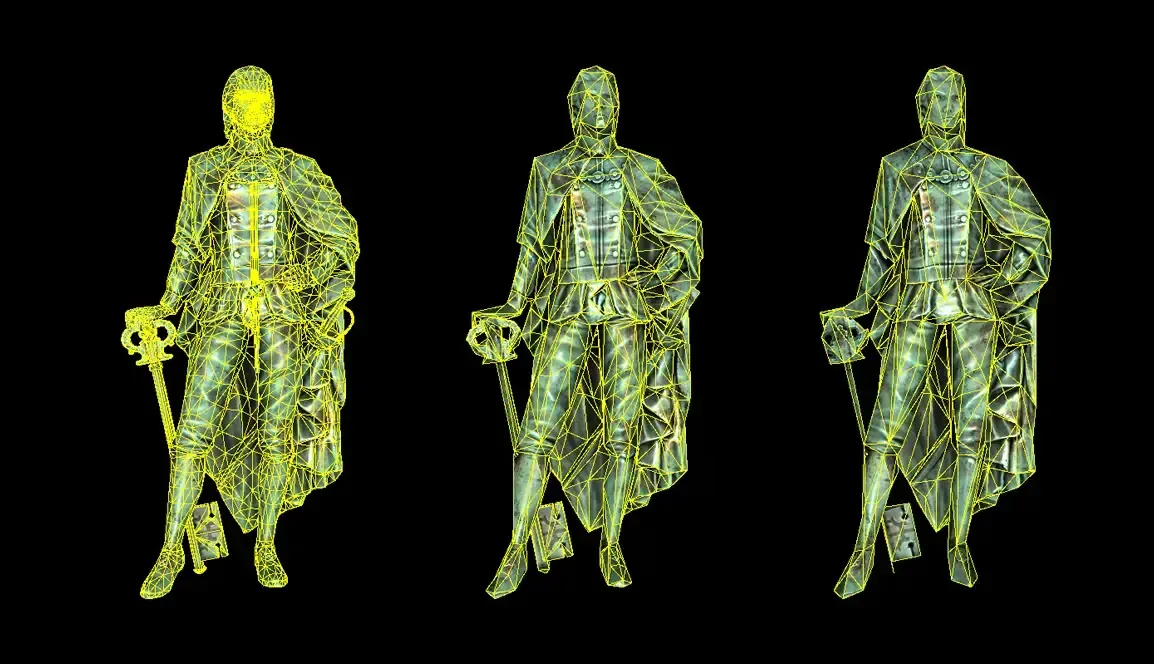
Some of them have Unity integrations that let you generate these meshes within the editor.
They are useful for doing quick performance tests and some results might work for production quality level. Very handy tools to have for us programmers.
C) Quick & Dirty LOD Generation
If you can approximate a specific LOD level with a 2d image, you can be sneaky about it.
Just make an in-game screenshot of your target object, tweak it as you need and assign it to a new LOD level with a quad on it. You might need to give it an unlit shader to make it look as intended, but you get the idea.
In live lesson #3 of the Performance Taskforce, I show you how to do this within the 1-minute mark.
You'll be impressed at the results.
Ok, so let's assume you have your new LOD meshes. Now we have to....

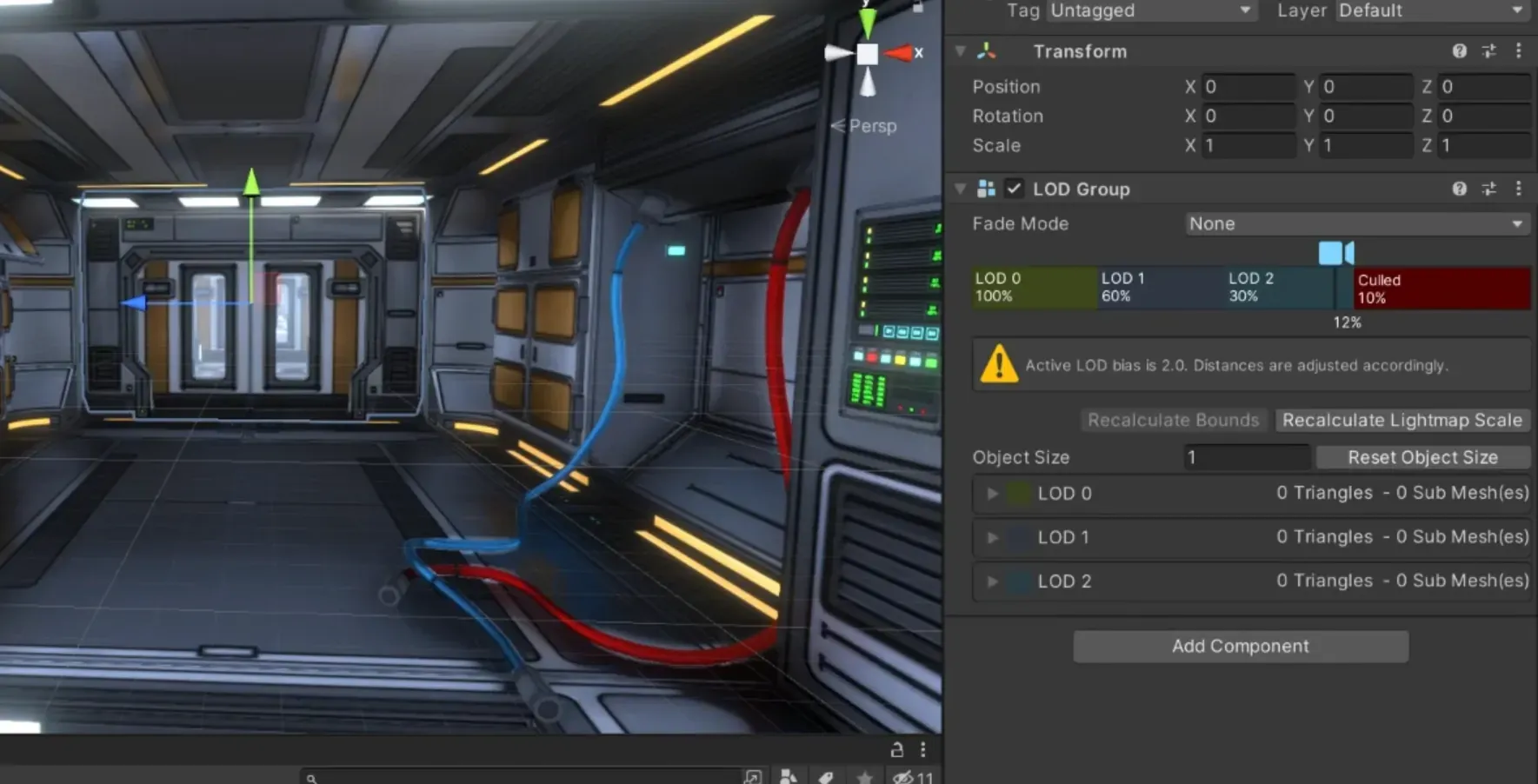
2. Add Your Unity LOD Group Component
Create an empty game object and add the LOD Group component into it.
That's it.

3. Setting Up LOD Levels
Now, it's time to tell Unity what meshes to use.
Again, this is straight forward. For each LOD level you want to have:
- Create an empty game object. This should be a child of the gameobject containing your new LOD Group.
- As usual, set up your game object to have its mesh filter and mesh renderer.
- In your LOD Group, drag the new child game object into the LOD level you want it to be in. If you don't have one, you can create a new LOD level by right-clicking on the horizontal bar.
That's it.
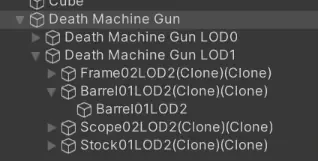
Once you have all your LOD levels set up, you need to tweak its distance thresholds.
4. Tweaking Distance Thresholds
Having multiple LOD levels won't help you if they are used at the wrong distances.
Here, we want to change the distances at which the different LODs are swapped.
You can do this by dragging the vertical bars that separate your LOD levels in the horizontal bar you have in your LOD Group.
These distances are measured in % related to the vertical size they represent on the screen. This is not an important detail to know, but be aware that these distances are also related to the size of your object.
LOD Distance Transition Tweaking
And that's it!
If you did these steps right, you will have LODs set up correctly for that mesh of yours that was causing trouble. You'll get a neat performance boost from applying LODs to further troublesome assets.
Now, that's not all... Let's get into the juicier stuff.
LODs & Advanced Workflows
LOD Settings in Unity
There are two project-wide settings in Unity you must be aware of:
- Unity LOD Bias: this is a modifier that helps you favor or penalize higher LOD levels. Think of this as a divider of the distance. Values closer to 0 favor higher LOD levels (i.e. low-poly models).
- Unity Max LOD Level: this sets an absolute ceiling to the maximum LOD level you can use. If you set it to 2, for example, you won't use any mesh that is more detailed to that.
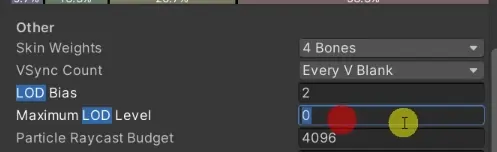
These settings have their uses:
- Performance checks: you can quickly change those to see if that affects your frame-rate. If so, then you were probably GPU bound by the vertex stage.
- Low-powered devices: you can adjust the limits so that your project run better on low-powered hardware.
You can find creative ways of using these settings in your project :-)
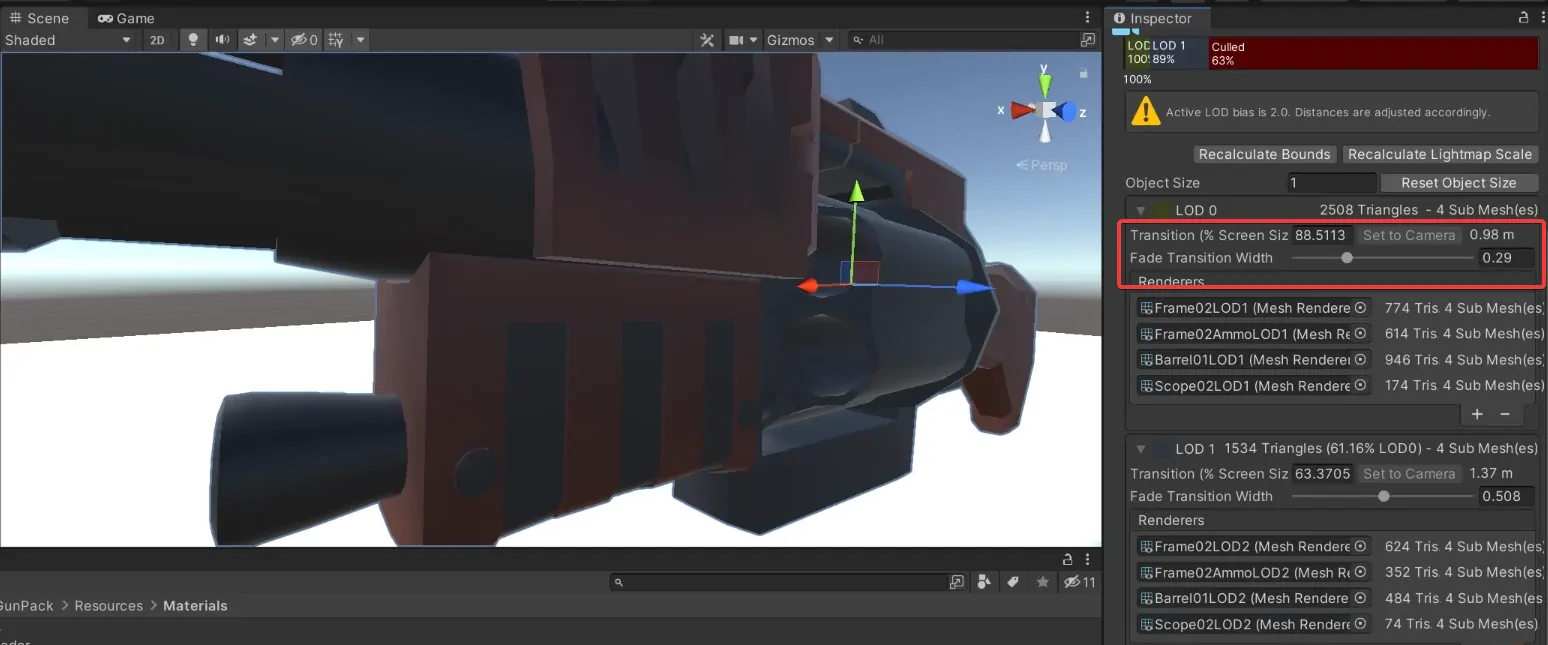
LOD Crossfading in Unity: Fix That LOD Popping Through Dithering!
Ok, LOD popping is one of the most visually annoying parts of using LODs in Unity.
LOD Popping happens when your user is able to see the abrupt transitions between LOD levels. This happens when your LOD levels are very different and the swaps change in noticeable moments.
To combat this, you can do two things:
- Add more LOD levels, although this increases your memory usage (more meshes).
- Crossfade: gradually transition between LOD levels.
Crossfading is just that, to do a smooth transition between your LOD levels instead of a rough, binary swap.
There are two main ways to achieve crossfading:
- Dithering: this technique uses alpha clipping to discard some pixels of the object. The more pixels you discard, the less visible it is.
- Transparency: you can set an alpha value to your objects between 0 and 100%.
Here's how dithering looks:
LOD Crossfading: Dithering
Both transitions may happen over time or over a distance overlap threshold. You can set that in your LOD levels in the LOD Group itself.
Crossfading has two challenges:
- You need to enable support for it in your shaders... manually. You can do this by altering the original standard shader, for example. And here is an old shader that works.
- It adds performance overhead due to pixel discarding or transparency.
But if you know what you are doing and measure its cost, you will please your users and still be within your performance budget.
In live lesson #3 of Performance Taskforce, I show you the simplest way to achieve the crossfading you want... to never make your players suffer from LOD popping ever again.
You might be wondering: what are the side effects of using LODs in your project?

LOD Compatibility
Lightmapping & LODs in Unity
Are LOD levels compatible with lightmap baking?
Yes, they are.
Each LOD will have its own lightmap as you can see below. This will indeed incur in higher memory overhead if you end up with more lightmaps, so that's another reason to be careful not to add too many LOD levels.
What about draw call batching?

Draw-Call Batching & LODs in Unity
How does using the Unity LOD affect draw call batching in Unity?
That's a tough one.
The thing is, LOD levels usually have different geometry. And different geometry means, different draw calls.
Unless some sort of batching kicks in.
Which sort of batching can work? Let's analyze some techniques.
- Static batching: in my experience, it works to some degree, but there are many factors that may break it such as having different lightmaps, light probes, etc..
- Dynamic batching: this may work, but you will hardly be able to meet its strict requirements regarding vertex attribute count. So you can't really trust this one.
- GPU Instancing: this method works with draw calls having the same mesh. So you each unique LOD level won't batch with each other, but multiple objects having the same LOD level will do. In other words: it might work if you have many instances of the same LODGroups, but it won't be perfect. A bad case for a specific prefab instance would be to have as many draw calls as LOD levels it has.
- SRP Batcher: nope, it doesn't do a good work in terms of batching with different LOD levels. However, these draw calls tend to be cheaper than their non-SRP equivalent. So make sure to test real-world performance for your use case.
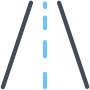
So keep batching in mind when you implement LODs in your Unity level. As always, measure your draw calls with the frame debugger.
Oh, another thing to keep in mind is occlusion culling.

Occlusion Culling
Here we are, the art of skipping the rendering of objects that are occluded by others.
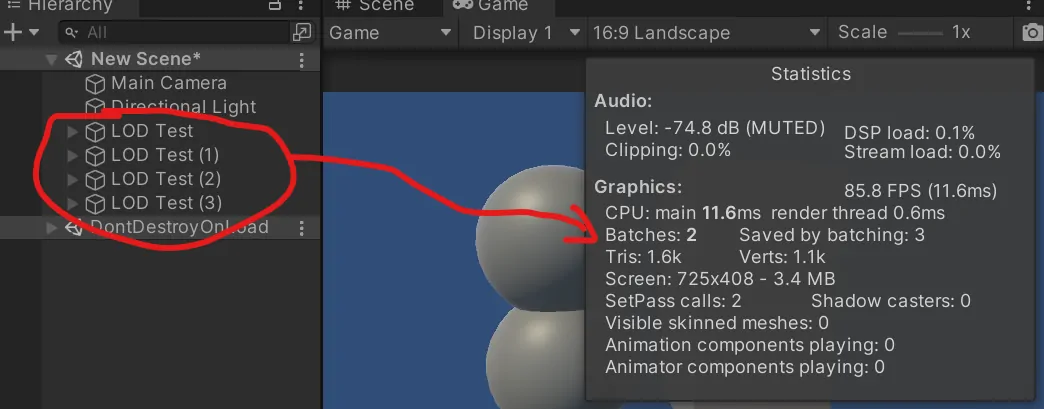
In this case, when you bake occlusion culling, you must be aware that Unity does so by taking only LOD0 into account. That is, Unity uses the most detailed LOD level to calculate the visibility cells for further culling.
Normally, this will be fine for you. However, if your LOD levels differ greatly in shape and volume, then you might end up drawing more objects than you need (performance overhead but visually correct) or fewer objects than you should (visually incorrect, better performance).
For example, the usage below would be pretty inefficient for occlusion culling due to shapes differing greatly across LOD levels:
Let's get into one of the hidden uses of LODs in Unity: saving draw calls.

Reducing Draw Calls With LODs in Unity
Not only can you reduce vertex count, you can also reduce draw calls.
How?
Two ways:
- Less-detailed LOD level can have simpler shaders and fewer materials.
- You can cull at certain distance.
This will give you substantial gains in CPU performance, especially in the area of rendering (the big green block you see in the profiler). You can see an example on how I do this in the lesson #3 of the Performance Taskforce.
So that was it for the more advanced usage of LODs.
And Now?
As you saw, the Unity LOD system can give you substantial benefits in two main areas:
- GPU Performance: especially by reducing vertex count.
- CPU Performance: you can reduce draw calls as well, which will lower your cost in the rendering section.
If you want to see a previous live session on LODs that goes deep into the how to of its advanced use cases, such as crossfading, make sure to enroll and watch week 3 of the Unity Performance Taskforce.
Ruben (The Gamedev Guru)

